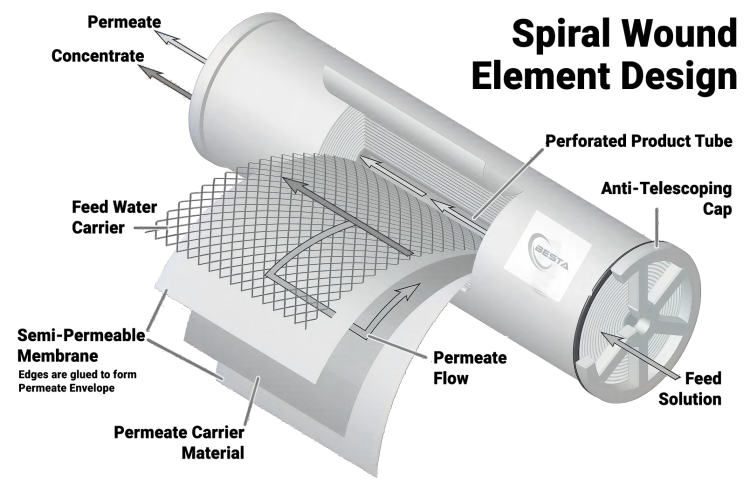
Reverse osmosis (RO) membrane filtration systems are widely used for water purification. However, several factors can influence their performance. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing system efficiency and longevity.
1. pH Level
The pH level of the feed water significantly impacts RO membrane performance. Membranes typically operate best within a pH range of 6 to 8. Outside this range, membrane degradation can occur. For example, at low pH levels, membranes may suffer from hydrolysis, while high pH levels can cause scaling.
| pH Level | Effect on Membrane |
|---|---|
| < 6 | Hydrolysis |
| 6-8 | Optimal Performance |
| > 8 | Scaling |
2. Recovery Rate
The recovery rate, or the percentage of feed water converted to permeate, affects membrane fouling and scaling. Higher recovery rates increase the concentration of dissolved solids, leading to potential scaling and fouling issues.
| Recovery Rate | Effect on Membrane |
|---|---|
| < 50% | Low Fouling Risk |
| 50-75% | Moderate Risk |
| > 75% | High Fouling Risk |
3. Feed Water Temperature
Temperature influences water viscosity and membrane permeability. Higher temperatures increase permeability but can also accelerate membrane degradation. The optimal temperature range is typically between 20°C and 30°C.
| Temperature (°C) | Effect on Membrane |
|---|---|
| < 20 | Reduced Permeability |
| 20-30 | Optimal Performance |
| > 30 | Increased Degradation |
4. Salt Concentration
High salt concentrations in feed water increase osmotic pressure, reducing system efficiency. Membranes are designed to handle specific salt concentrations, and exceeding these limits can lead to poor performance.
| Salt Concentration (ppm) | Effect on Membrane |
|---|---|
| < 500 | Optimal Performance |
| 500-2000 | Moderate Impact |
| > 2000 | Reduced Efficiency |
5. Feed Water Pressure
Operating pressure is critical for RO systems. Higher pressures improve water flux but can also increase energy consumption and membrane stress. The optimal pressure range depends on the specific membrane and application.
| Pressure (psi) | Effect on Membrane |
|---|---|
| < 200 | Low Flux |
| 200-400 | Optimal Performance |
| > 400 | High Energy Use |
Conclusion
Optimizing RO membrane performance requires careful consideration of pH levels, recovery rates, feed water temperature, salt concentration, and operating pressure. By monitoring these factors and making necessary adjustments, you can ensure efficient and long-lasting system operation.

 MBR Membrane
MBR Membrane Reverse Osmosis Membrane
Reverse Osmosis Membrane Residential Ro Membrane
Residential Ro Membrane UF Membrane
UF Membrane Water Treatment Plant
Water Treatment Plant Residential Ro Machine
Residential Ro Machine Brackish Ro System
Brackish Ro System Sea water system/SW RO plant
Sea water system/SW RO plant Bag Filter
Bag Filter Cartridge Filter
Cartridge Filter Commercial Water Filtration System
Commercial Water Filtration System Membrane Cleaning System(CIP)
Membrane Cleaning System(CIP) Consumables Accessories
Consumables Accessories