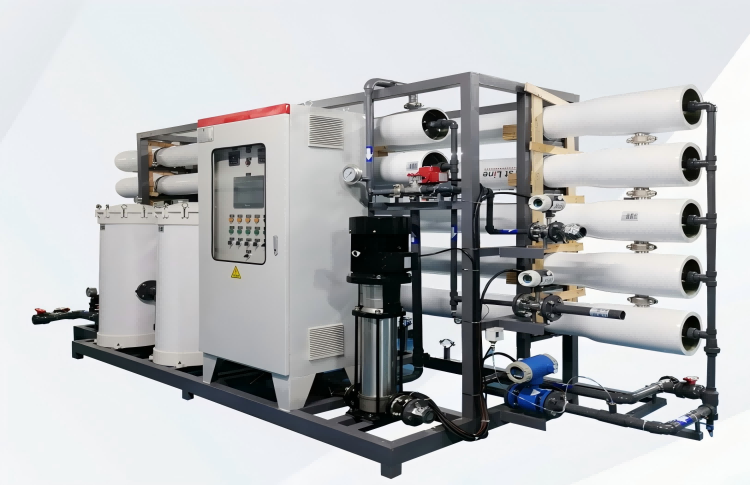
Desalination is an important solution in areas where there is a shortage of fresh water. Among the various desalination methods, ósmosis inversa (RO) is the most common technology for converting seawater into drinking water. The process relies on semi-permeable membranes to remove salts and other impurities from seawater.
How Does Reverse Osmosis Work in Desalination?
- Seawater intake: Seawater is pumped into a desalination plant, where it goes through a filtration process to remove large particles, arena, y escombros.
- Pretratamiento: The water is then pre-treated to remove smaller particles, microorganismos, and chemicals such as chlorine, which can damage the RO membrane.
- Reverse osmosis process: Pretreated seawater is forced through a semi-permeable membrane under high pressure. The membrane only allows water molecules to pass through, while salts and contaminants are retained, resulting in fresh water.
- Post-tratamiento: Desalination water is post-treated to adjust pH, add essential minerals, and ensure that the water meets drinking water standards.
Reverse osmosis principle
The basic principle of reverse osmosis is to apply pressure to seawater, forcing water molecules through a membrane while repelling salts and other impurities. This process results in clean drinking water. RO is highly effective, removing up to 99% of salts, bacterias, and other contaminants.

 Membrana MBR
Membrana MBR Membrana de ósmosis inversa
Membrana de ósmosis inversa Membrana RO residencial
Membrana RO residencial Membrana UF
Membrana UF Planta de tratamiento de agua
Planta de tratamiento de agua Máquina residencial RO
Máquina residencial RO Sistema RO salobre
Sistema RO salobre Sistema de agua de mar/planta SW ro
Sistema de agua de mar/planta SW ro Filtro de bolsa
Filtro de bolsa Filtro de cartucho
Filtro de cartucho Sistema de filtración de agua comercial
Sistema de filtración de agua comercial Sistema de limpieza de membrana(Titubear)
Sistema de limpieza de membrana(Titubear) Accesorios de consumo
Accesorios de consumo
