En este artículo, Lo guiaremos a través del proceso integral que hemos desarrollado para operar y optimizar sistemas de ósmosis inversa (RO).. Con los años de experiencia y conocimientos de Besta en la industria del tratamiento de agua., Nuestro enfoque simplificado garantiza la máxima eficiencia., calidad del agua constante, y prácticas sustentables. Si es nuevo en la tecnología RO o busca mejorar su sistema actual, Esta guía proporcionará información valiosa sobre nuestras metodologías probadas..
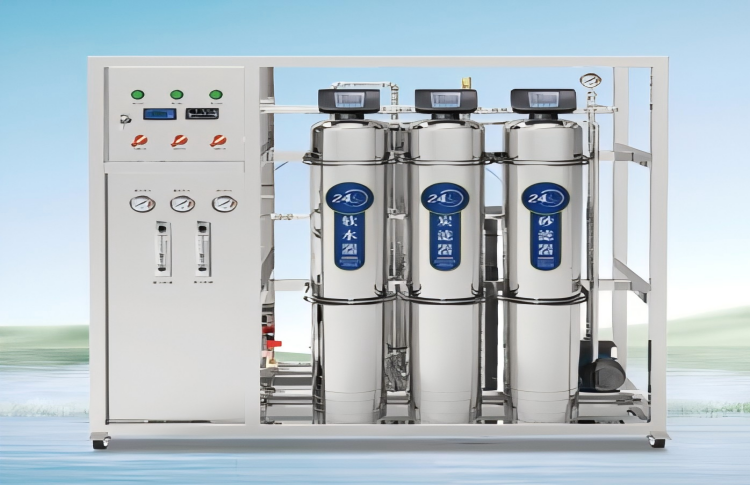
Equipos de ósmosis inversa Proceso de filtración
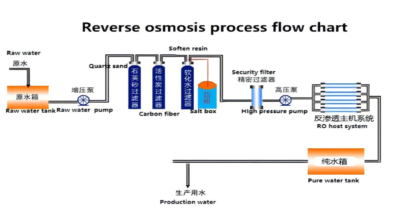
Gráfico de flujo de proceso de ósmosis inversa
- Tanque de agua crudo
El tanque de agua cruda almacena y amortigua el agua entrante., Garantizar un suministro de agua estable y adecuado para todo el sistema.. Sin tanque de agua bruta, Las fluctuaciones de presión y flujo durante el uso pico pueden alterar la estabilidad de los equipos posteriores.. Típicamente, La capacidad del tanque debe ser 1 a 1.5 veces el uso de agua del sistema o al menos suficiente para proporcionar 15 minutos de operación. Un controlador de nivel en el tanque regula la apertura y el cierre de la válvula solenoide de entrada y la bomba de agua cruda.. Por ejemplo, cuando el nivel del agua es bajo, La válvula solenoide se abre para el llenado automático.. Una vez que el agua alcanza un nivel alto establecido, la válvula deja de llenarse, y la bomba deja de funcionar cuando el nivel del agua es bajo. - Bomba de agua cruda
La bomba de agua cruda extrae agua del tanque y aumenta la presión para cumplir con los requisitos de los procesos de tratamiento posteriores.. Esta bomba funciona junto con el sensor de nivel de agua en el tanque de agua cruda para evitar que se seque y cause daños.. Los componentes de la bomba están fabricados de acero inoxidable SUS304 duradero para un rendimiento duradero.. - Filtro multimedia
El filtro multimedia utiliza arena de cuarzo como medio de filtración para eliminar impurezas particuladas y sólidos suspendidos.. Cuando el agua pasa a través del medio filtrante., los huecos actúan como un tamiz, atrapando partículas en la superficie. Con el tiempo, A medida que la superficie del filtro recoge más impurezas., El diferencial de presión a través del filtro aumenta., señalando la necesidad de retrolavado. El retrolavado elimina las impurezas atrapadas y restaura la función del filtro., Garantizar un rendimiento eficiente y continuo.. - Filtro de carbono activado
Los filtros de carbón activado dependen de las propiedades de adsorción del carbón para eliminar contaminantes orgánicos., microorganismos, cloro, metales pesados, y otros contaminantes. Este proceso también ayuda a la degradación microbiana de la materia orgánica., Reducir la demanda química de oxígeno. (BACALAO). Este filtro también elimina los olores., bandera, y detergentes sintéticos. Como pretratamiento para sistemas de RO, Los filtros de carbón activado ayudan a prevenir la contaminación orgánica de las membranas de RO y siguen siendo efectivos a diferentes temperaturas., ph, y condiciones orgánicas. El tanque de filtro, hecho de plástico reforzado con fibra de vidrio (FRP), está diseñado para alta resistencia, resistencia a la corrosión, y una larga vida útil. - Filtrante
Los filtros suavizantes mejoran la tasa de recuperación de los sistemas de ósmosis inversa al evitar la formación de incrustaciones debidas a los iones de calcio y magnesio.. Estas escalas, como CaCO₃ y CaSO₄, puede dañar los equipos posteriores y disminuir la eficiencia operativa. El filtro utiliza una resina de intercambio catiónico de ácido fuerte para reemplazar Ca²⁺ y Mg²⁺ con iones de sodio.. Cuando la resina se satura, Es necesaria la regeneración con sal industrial.. El sistema de control automático del filtro gestiona el proceso de regeneración., que ocurre aproximadamente cada 24 horas e incluye múltiples etapas: correr, retrolavado, regeneración, enjuague lento, enjuague rápido, y rellenando el tanque de sal. Este sistema garantiza un continuo, ablandamiento efectivo. - Filtro de seguridad
El filtro de seguridad elimina partículas más grandes que 5 µm, evitando que dañen los módulos de membrana RO o la bomba de alta presión. Esta protección es esencial ya que los desechos pueden provocar fugas de sal y contaminación cruzada., impactando negativamente la calidad del agua. El filtro opera entre 0.2 MPa y 0.5 MPA. Cuando la diferencia de presión entre la entrada y la salida excede el límite establecido, normalmente 0,05–0,07 MPa, Es necesario reemplazar el cartucho del filtro para evitar daños por obstrucción.. - Bomba de alta presión
La bomba de alta presión proporciona la presión necesaria para que funcionen las membranas de RO. Este sistema utiliza una bomba centrífuga vertical de alta calidad fabricada en acero inoxidable SUS304.. La bomba es conocida por su diseño compacto., bajo ruido, bajos costos operativos, y larga vida útil, garantizando un rendimiento fiable y eficiente. - Ósmosis inversa (RO) Sistema
RO es un proceso impulsado por presión que fuerza el agua a través de una membrana semipermeable., separar el agua de los solutos. Este método reduce la concentración de impurezas y mejora la pureza del agua., alcanzar tasas de desalinización superiores 98%. Los sistemas de RO son eficaces para tratar agua de diversas salinidades y ofrecen excelentes beneficios técnicos y económicos.. Aunque inicialmente limitado por el costo, Las recientes reducciones de precios han hecho que la tecnología de ósmosis inversa sea ampliamente accesible para proyectos de desalinización y purificación de agua.. Membranas RO, el núcleo del sistema, quitar más 98% de iones de agua, bacterias, coloides, y grandes moléculas orgánicas. - Tanque de agua
El tanque de agua almacena agua filtrada., ponerlo a disposición para su uso o distribución posterior.
En Besta Membrane Technology, Estamos comprometidos a ofrecer soluciones de tratamiento de agua de última generación que satisfagan diversas necesidades.. Nuestro proceso de equipos de ósmosis inversa es el resultado de una investigación meticulosa y experiencia práctica., asegurando confiabilidad y rendimiento. Siguiendo estos pasos, puede lograr una calidad superior del agua y una eficiencia operativa a largo plazo. Si tienes alguna duda o buscas soluciones a medida, nuestro equipo está aquí para ayudarle. Juntos, Hagamos que el agua potable sea accesible para todos.!

 Membrana MBR
Membrana MBR Membrana de ósmosis inversa
Membrana de ósmosis inversa Membrana RO residencial
Membrana RO residencial Membrana UF
Membrana UF Planta de tratamiento de agua
Planta de tratamiento de agua Máquina residencial RO
Máquina residencial RO Sistema RO salobre
Sistema RO salobre Sistema de agua de mar/planta SW ro
Sistema de agua de mar/planta SW ro Filtro de bolsa
Filtro de bolsa Filtro de cartucho
Filtro de cartucho Sistema de filtración de agua comercial
Sistema de filtración de agua comercial Sistema de limpieza de membrana(Titubear)
Sistema de limpieza de membrana(Titubear) Accesorios de consumo
Accesorios de consumo
