Introduction
Ultrafiltration (UF) systems play a crucial role in the water treatment industry. Their ability to remove microscopic particles makes them essential for applications like drinking water purification and industrial wastewater management. This article will explore the technology behind ultrafiltration, its benefits, and its growing global adoption.
What Is Ultrafiltration?
Ultrafiltration uses semi-permeable membranes with pore sizes ranging from 0.01 to 0.1 microns. These membranes effectively filter out suspended particles, bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants while allowing water and dissolved minerals to pass. Unlike reverse osmosis (RO), UF focuses on removing particles rather than dissolved solids. Consequently, UF systems maintain water’s essential minerals.
Applications and Benefits
First, in drinking water treatment, UF systems remove harmful pathogens and contaminants without using chemicals, ensuring safe, clean water. Additionally, in industrial settings, UF supports wastewater recycling, reducing operational costs while meeting environmental regulations. Moreover, UF membranes often serve as a pre-treatment step in seawater desalination plants, protecting and enhancing the efficiency of RO systems.
Transition to Data: Market Trends and Growth
The global UF market is expanding rapidly due to water scarcity, environmental regulations, and technological advancements. For instance, experts predict the market will grow at a CAGR of 9.4% from 2024 to 2029, reaching a value of $8.2 billion
Key Data Table: Market Growth
| Year | Market Value (USD Billion) | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 4.9 | 9.4 |
| 2029 | 8.2 |
Technology Overview
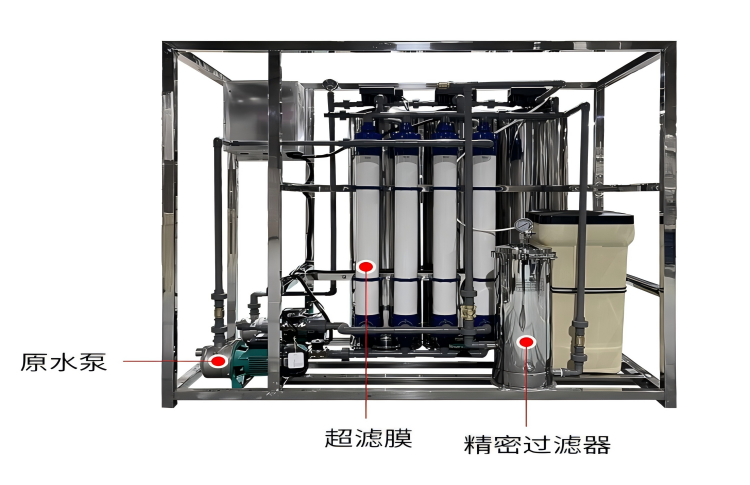
UF systems commonly consist of hollow fiber membranes arranged in modules. Water flows through the membranes, trapping contaminants. These systems stand out for their energy efficiency and minimal maintenance compared to traditional methods. Importantly, they contribute to sustainable water management by supporting water reuse and reducing chemical treatments.
Comparison Table: UF vs. Other Technologies
| Feature | Ultrafiltration | Reverse Osmosis | Carbon Filters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pore Size (Microns) | 0.01–0.1 | ~0.0001 | ~1 |
| Removes Dissolved Solids | No | Yes | No |
| Energy Consumption | Low | High | Low |
Environmental Impact
UF systems align with sustainable practices by minimizing chemical usage and enabling water reuse. The durability of UF membranes also reduces waste and lowers the environmental footprint. By adopting this technology, industries can contribute to more sustainable water management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ultrafiltration systems offer efficient, versatile, and sustainable solutions for water treatment. As industries and municipalities work to overcome water challenges, UF technology stands as a significant player in future water solutions.

 MBR Membrane
MBR Membrane Reverse Osmosis Membrane
Reverse Osmosis Membrane Residential Ro Membrane
Residential Ro Membrane UF Membrane
UF Membrane Water Treatment Plant
Water Treatment Plant Residential Ro Machine
Residential Ro Machine Brackish Ro System
Brackish Ro System Sea water system/SW RO plant
Sea water system/SW RO plant Bag Filter
Bag Filter Cartridge Filter
Cartridge Filter Commercial Water Filtration System
Commercial Water Filtration System Membrane Cleaning System(CIP)
Membrane Cleaning System(CIP) Consumables Accessories
Consumables Accessories