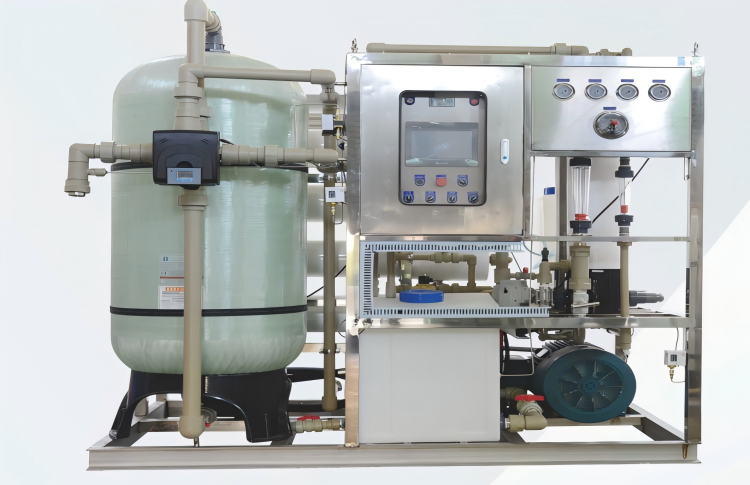
When sailing on the vast ocean, access to fresh water is crucial for both crew and operations. Marine reverse osmosis (RO) desalination equipment has become an essential solution for ships and vessels. However, selecting the right equipment can be challenging without proper guidance. This article offers clear, actionable advice to help you make an informed choice.

Marine Reverse Osmosis Desalination Equipment
1. Understand Your Water Demand
First and foremost, evaluate the daily water consumption on your vessel. A fishing boat may require 1,000–2,000 liters per day, while larger cargo ships might need over 20,000 liters. To illustrate, here’s a quick reference:
| Vessel Type | Daily Water Demand (Liters) |
|---|---|
| Small Fishing Boat | 500–5,000 |
| Cargo Ship | 5,000–20,000 |
| Cruise ship | 20,000–100,000 |
Knowing your water demand ensures you choose a system with adequate capacity, avoiding underperformance or overspending.
2. Evaluate Water Quality
Next, assess the salinity of the seawater where your vessel operates. Coastal waters often have salinity levels between 10,000 and 35,000 ppm, while open-ocean water can reach 45,000 ppm. A high-salinity environment demands a robust RO system capable of handling extreme conditions.
3. Choose the Right Size and Efficiency
Moreover, consider the size and efficiency of the equipment. Compact systems save valuable space on your vessel, but they must still meet performance standards. Look for energy-efficient models to reduce operational costs.
For instance, high-efficiency marine RO units typically consume 3–5 kWh per cubic meter of water produced, compared to older systems that may use 8 kWh or more.
4. Pay Attention to Materials
Durability is another key factor. Because marine RO systems operate in corrosive environments, stainless steel and corrosion-resistant materials are essential. Opt for components like titanium pumps and fiberglass-reinforced pressure vessels for extended lifespan and reliability.
5. Available Treatment
| TYPE | Output water(Ton/Day) | Desalinating(Rate%) | TDS (mg/L) | Operation Pressure (Mpa) |
Power Consumption (KW) |
Net Weight (kg) |
Size (LxWxH) |
| BM-FSHB0.5 | 0.5 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 0.75 | 15 | 680x250x350 |
| BM-FSHB1.5 | 1.5 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 1.1 | 100 | 800x500x650 |
| BM–FSHB3 | 3 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 1.5 | 150 | 500x570x1350 |
| BM-FSHB5 | 5 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 2.2 | 400 | 910x500x1540 |
| BM-FSHB10 | 10 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 5.5 | 600 | 1520x780x1935 |
| BM-FSHB20 | 20 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 10 | 900 | 1520x830x2025 |
| BM-FSHB30 | 30 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 15 | 1200 | 2440x1000x2120 |
| BM-FSHB40 | 40 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 15 | 1600 | 2300x1100x2310 |
| BM-FSHB50 | 50 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 18.5 | 2000 | 2300x1100x2310 |
| BM-FSHB60 | 60 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 21 | 2200 | 2350x1200x2300 |
| BM-FSHB100 | 100 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 45 | 4500 | 5000x2000x1900 |
| BM-FSHB200 | 200 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 60 | 5500 | 5000x2000x1900 |
| BM-FSHB500 | 500 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 110 | 1450 | 9500x2000x2000 |
| BM-MHB2000 | 2000 | 99.2 | <700 | 3.5-5.5 | 350 | 45000 | 15000x10000x3500 |
6. Consider Maintenance and Support
In addition, evaluate the maintenance requirements and availability of technical support. Choose systems with easy-to-clean membranes and accessible spare parts to minimize downtime. Reliable after-sales service can be a lifesaver, especially during long voyages.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right marine RO desalination equipment involves assessing water demand, salinity, size, efficiency, materials, certifications, maintenance needs, and budget. By following these guidelines, you can ensure a reliable and cost-effective freshwater supply for your vessel, enhancing operations and crew satisfaction.

 MBR Membrane
MBR Membrane Reverse Osmosis Membrane
Reverse Osmosis Membrane Residential Ro Membrane
Residential Ro Membrane UF Membrane
UF Membrane Water Treatment Plant
Water Treatment Plant Residential Ro Machine
Residential Ro Machine Brackish Ro System
Brackish Ro System Sea water system/SW RO plant
Sea water system/SW RO plant Bag Filter
Bag Filter Cartridge Filter
Cartridge Filter Commercial Water Filtration System
Commercial Water Filtration System Membrane Cleaning System(CIP)
Membrane Cleaning System(CIP) Consumables Accessories
Consumables Accessories
